Authentication setup
When working with Git, authentication is typically done through SSH. This means you need a pair of SSH keys (public and private). The public key is to give to any service you want to authenticate to (e.g. GitHub) and the private key stays on your computer and is used by your SSH program to prove that you are the owner of the corresponding public key.
If you already have a SSH key, you can skip to “Adding your public key to Git”
Creating SSH keys
To generate the SSH key pair we can use the tool ssh-keygen from OpenSSH.
OpenSSH is installed by default in most versions of Windows and Linux. If it is not enabled on your Windows system, see this page.
Use the following command, replacing the email with yours.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
This dialog should show up:

Press enter to save the key at the default path.
You will now be asked to enter a passphrase that you will need to use your private key.

Your SSH key pair will now be generated:
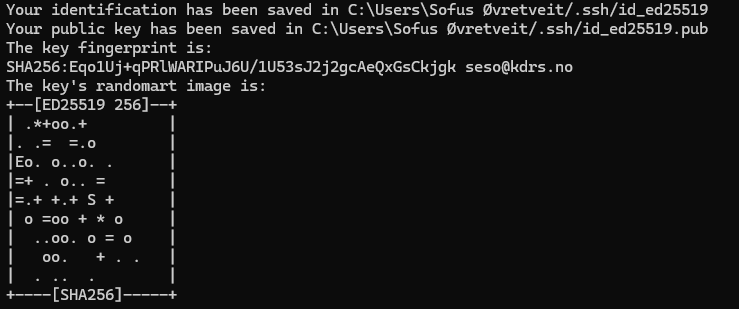
Your key pair will be stored at the following paths:
Windows: C:\Users\<username>\.ssh\
Unix: /home/<username>/.ssh/
The file id_ed25519 is your private key, and should stay on your local machine(s) and never be shared with anyone.
The file id_ed25519.pub is your public key, and should be shared with services you want to authenticate with.
Adding your public key to Git
Log in to maler.kdrs.no and click your profile picture in the top right corner

Click settings
Click SSH / GPG keys
Click Add key in the “Manage SSH keys” panel
Enter a title of your choice. Open your SSH public key (id_ed25519.pub) in a text editor and copy its contents to the content field.
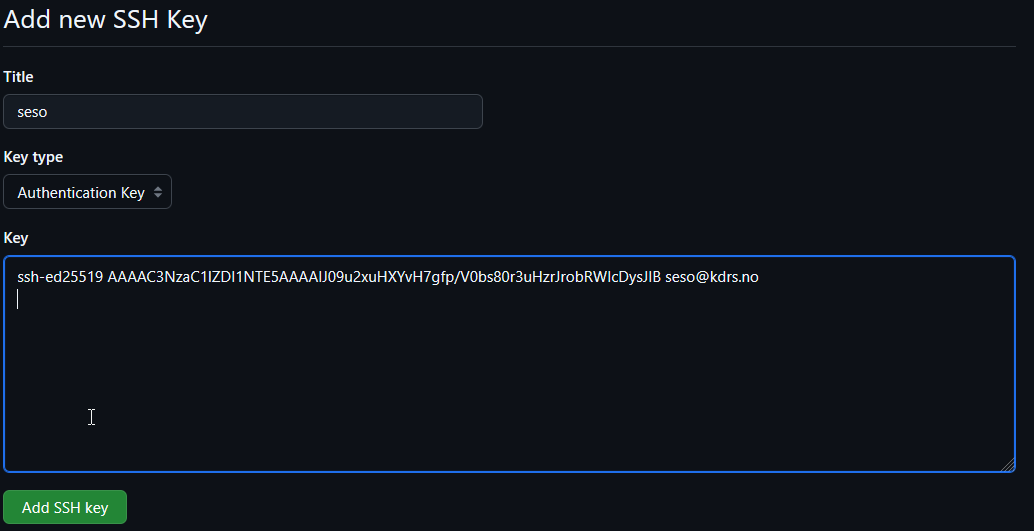
Click “Add SSH key”.
You are now able to authenticate with Git over SSH, on any machine where you private key (id_ed25519) is in your .ssh folder.
Adding your private key to another machine
If you need to connect to Git from a different machine, or a virtual machine, you need to transfer your SSH private key to that machine. Copy your id_ed25519 to the following directory:
Windows: C:\Users\<username>\.ssh\
Unix: /home/<username>/.ssh/
On Unix the SSH private key needs to not be readable by other users. This can be done with the following command:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519